Deploying LogicVein Appliances on Hyper-V
Hyper-V is a virtualization platform developed by Microsoft that allows users to create and manage virtual machines on their Windows operating systems.
To begin the Hyper-V setup, one must ensure that their system meets the necessary requirements. This includes having a compatible version of Windows installed, enabling virtualization in the BIOS settings, and having sufficient hardware resources such as RAM and disk space.
Users can start creating virtual machines using either Hyper-V Manager or PowerShell commands. It is important to allocate appropriate resources to each virtual machine based on its intended purpose. This includes assigning CPU cores, memory size, and storage space.
Additionally, network connectivity should be configured for each virtual machine to ensure proper communication within the network environment. This involves creating virtual switches and attaching them to specific network adapters.
Operating Environment:
| Item | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Virtualization Platform | ≥ VMWare ESXi 7.0 ≥ Hyper-V (Windows Server 2012 R2) |
| CPU | ≥ 8 cores |
| Memory | ≥ 8 GB |
| Hard Disk | HDD 1: 8 GB (system area) HDD 2: 50 GB or more (data area) |
| Supported Browsers (We recommend that you use the latest version of a compatible browser) | Google Chrome Mozilla Firefox Microsoft Edge |
Step-by-Step Hyper-V VM Setup
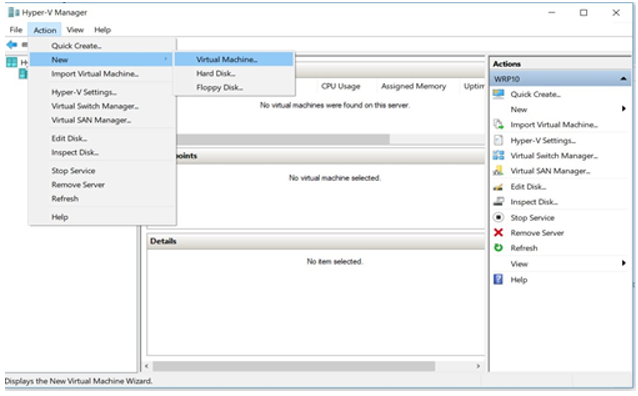
1. Launch the New Virtual Machine Wizard
Open Hyper-V Manager and navigate to
Action → New → Virtual Machine
to display the wizard.
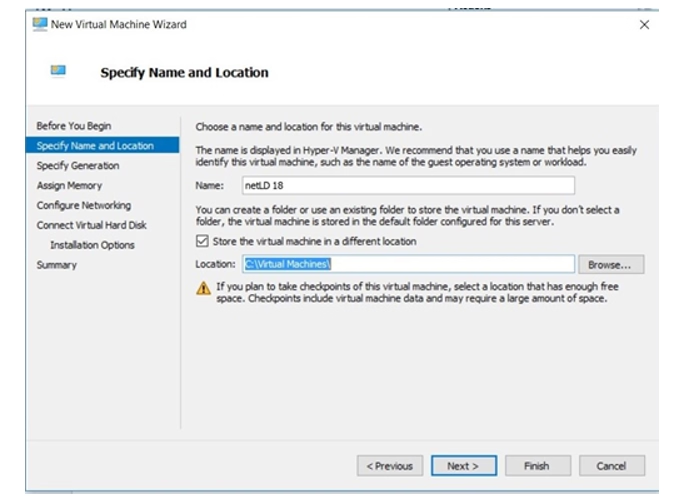
2. Name the Virtual Machine
Enter a name for the new VM.
Optionally change the storage location, then click Next.
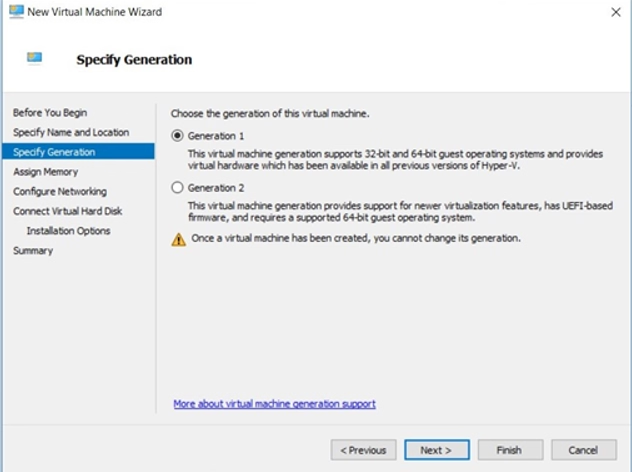
3. Choose the Generation
Select Generation 1 and click Next.
4. Configure Memory
Set the Startup memory value and click Next.
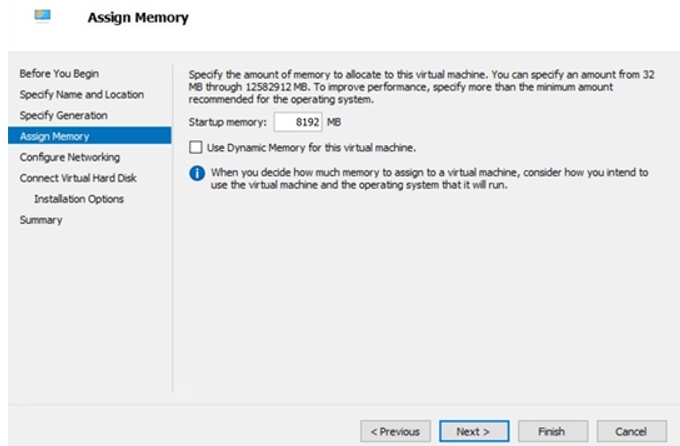
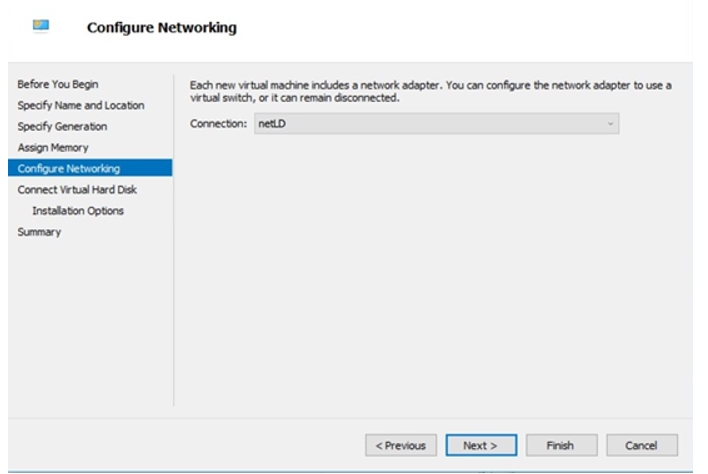
5. Configure Networking
Under Connection, select a virtual switch for the network connection, then click Next.
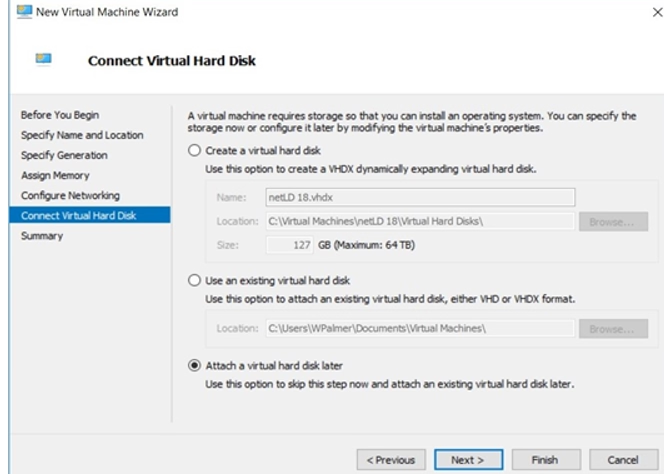
6. Skip Hard Disk Creation
Choose Connect virtual hard disk later and click Next.
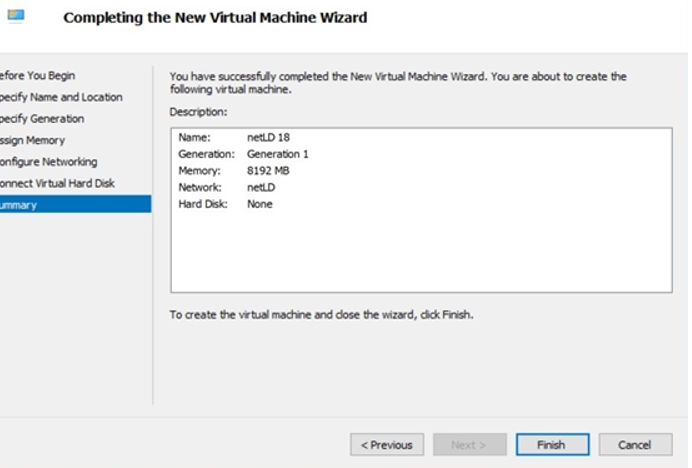
7. Finish the Wizard
Click Finish to create the new virtual machine.
8. Open VM Settings
Right-click the newly created VM and choose Settings.
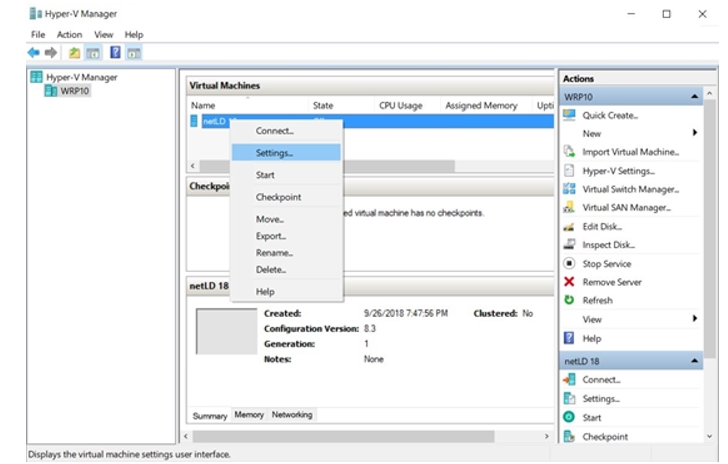
9. Adjust Processor Count
Select Processor and increase the Number of virtual processors as needed.
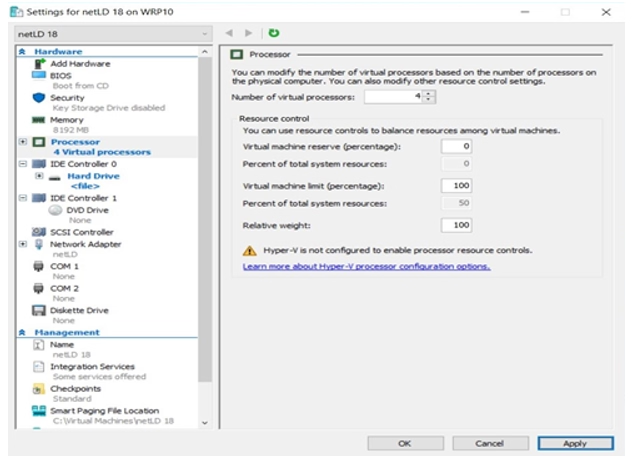
10. Add a Virtual Hard Disk
Under IDE Controller 0, select Hard Drive and click Add.
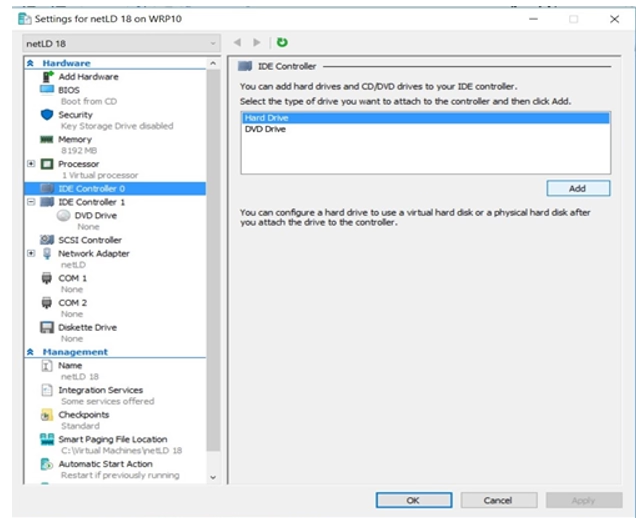
11. Browse for Disk
Click Browse to locate your .vhdx files.
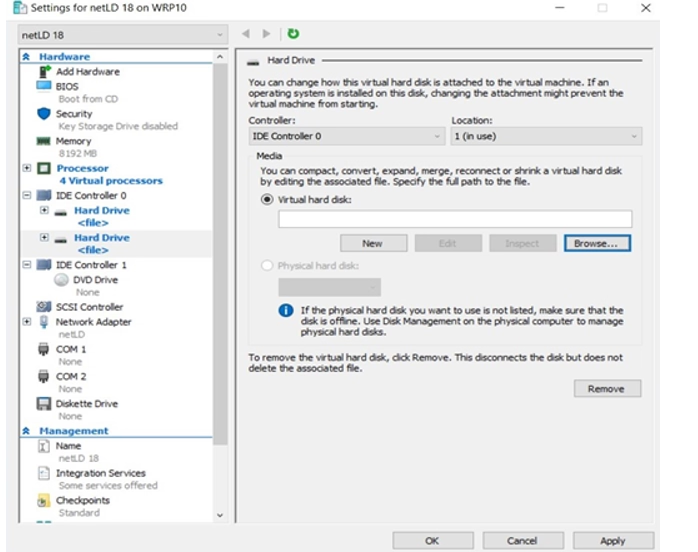
12. Attach Disk1
Browse to the folder where you saved the downloaded .vhdx files, select disk1.vhdx, and click Open.
13. Attach Additional Disks
Repeat steps 10–12 to add disk2.vhdx.
14. Configure Advanced Network Features
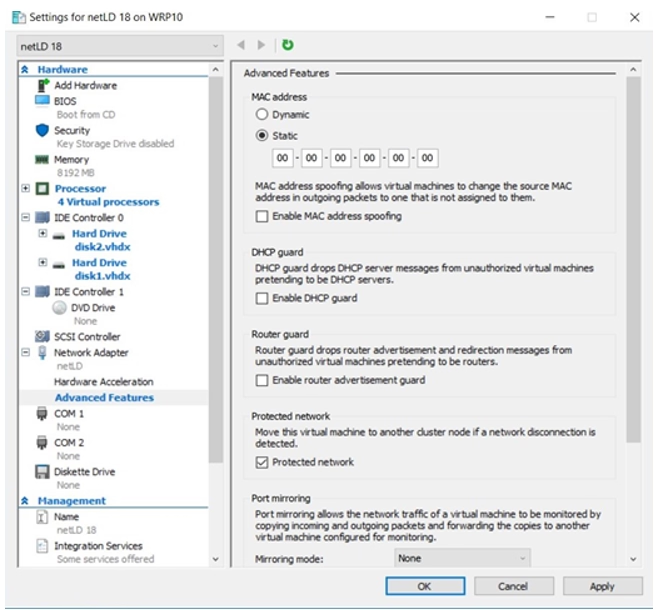
Expand the Network Adapter section, select Advanced Features, assign a Static MAC address, and click OK.
✅ Final Notes
- Using a static MAC ensures consistent network identification.
- Always size memory, CPU, and disk resources to match your workload needs.
- Generation 1 VMs are often chosen for compatibility, but Generation 2 can be used if supported by your OS.
After the deployment is completed, please [Start] and [Connect] to the virtual machine.
Final Takeaway
With LogicVein, you do not just react to changes — you control them.
Watch our series of videos here or see all our features here.
With its combination of discovery, monitoring, compliance, and automation, LogicVein transforms how IT teams manage complex network environments.
Whether you are looking to reduce manual work, improve network reliability, or gain better visibility into device configurations, LogicVein will provide you with the tools you need—all in a single platform.
Ready to see LogicVein in action? Request a Demo and discover how you can simplify operations, improve reliability, and gain full network visibility.
#LogicVein #SmartBridge #NetworkAutomation #NetworkManagement #NetworkCompliance #ChangeManagement #MSPTools #MultiVendorNetworks